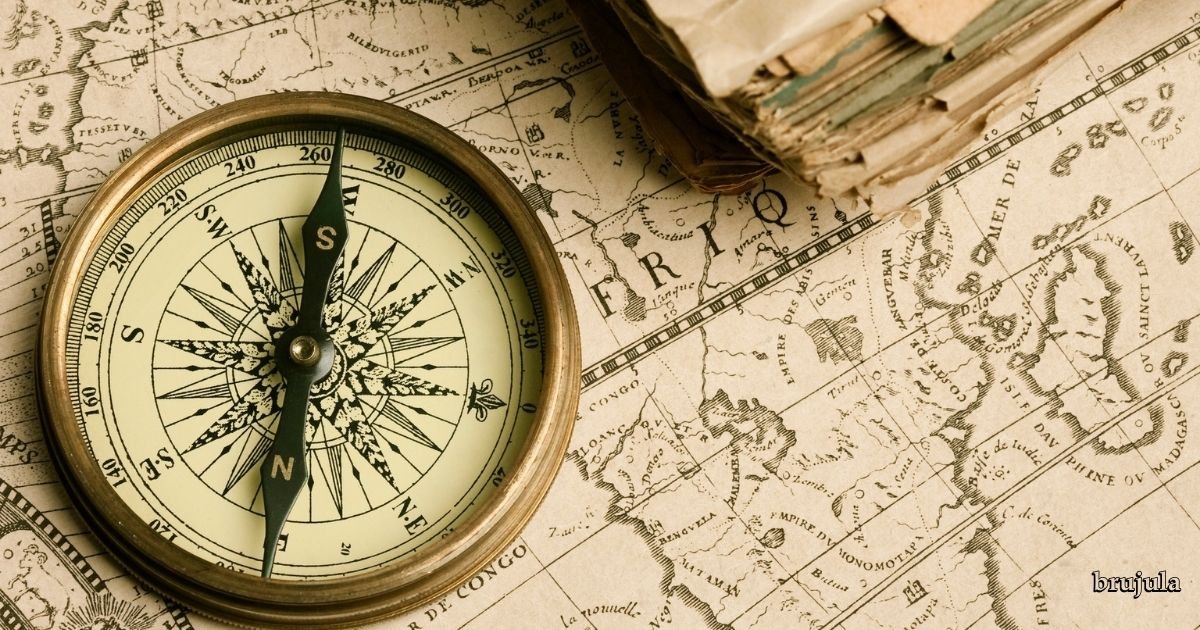
Compass is one of the most ancient and reliable tools for navigation, guiding travelers, sailors, and explorers for centuries. Whether you are hiking, sailing, or simply curious about how it works, understanding the fundamentals of a compass is both practical and fascinating.
What Is a Compass?
A compass is a navigational tool that shows direction relative to the Earth’s magnetic poles. It consists of a magnetized needle that aligns itself with the Earth’s magnetic field, pointing towards magnetic north. The most common type of compass is the magnetic compass, although there are also electronic and gyrocompasses used in modern navigation.
How Does a Compass Work?
The compass works by detecting the Earth’s magnetic field. Inside a basic magnetic compass, a lightweight, magnetized needle is mounted on a pivot so that it can spin freely. The needle always points towards the magnetic north, helping users determine directions like north, south, east, and west.
Parts of a Compass
Compass Needle
The needle is magnetized and freely rotates to point towards magnetic north. One end is usually marked (often red) to indicate the north.
Baseplate
The baseplate is the flat, transparent part of the compass that provides a stable surface for use on maps.
Direction of Travel Arrow
This arrow, located on the baseplate, indicates the direction in which the user should travel once the bearing has been set.
Rotating Bezel (Compass Housing)
The bezel is a movable ring that surrounds the compass needle and is marked with degrees from 0 to 360, representing the full circle of direction.
Types of Compasses
Magnetic Compass
The traditional magnetic compass, widely used in outdoor activities, aligns with the Earth’s magnetic field to provide reliable directions.
Lensatic Compas s
Used mainly by the military, this compas s is designed for precise navigation and includes a sighting lens for more accurate readings.
Gyrocompas s
This is an advanced compas s used in ships and aircraft. Instead of relying on magnetism, a gyrocompas s uses a fast-spinning wheel to align with true north, not magnetic north.
Digital Compas s
Digital compas ses are often found in smartphones, GPS devices, and smartwatches. They use sensors to detect magnetic fields and provide direction.
Understanding Magnetic North vs. True North
One important distinction in using a compas s is understanding the difference between magnetic north and true north. Magnetic north is where the compas s needle points, which aligns with the Earth’s magnetic field. True north, however, is the geographic North Pole. Depending on where you are in the world, there can be a slight difference between the two, known as magnetic declination.
How to Use a Compas s
Hold the Compas s Flat
Keep the compas s level and flat in your hand so the needle can move freely. Make sure there are no metal objects or electronic devices near, as they can interfere with the needle.
Align the Compas s with a Map
Place the compas s on a map and line up the baseplate’s edge with your intended route. Rotate the bezel until the orienting lines match the map’s grid.
Find Your Bearing
Once the compas s is aligned, turn your body until the needle points to the north. The direction-of-travel arrow will indicate your correct path.
Why Is a Compas s Still Useful Today?
Even in the age of GPS, a compas s remains an essential tool for outdoor enthusiasts. It does not rely on batteries, signals, or satellites, making it a dependable backup when navigating remote areas where technology might fail.
Conclusion
The compas s is a timeless tool that continues to guide adventurers and professionals alike. Whether you’re navigating in the wilderness or sailing across oceans, understanding how to use a compas s effectively can make all the difference in staying on course.
FAQs
What’s the difference between magnetic north and true north?
Magnetic north is the direction the compas s needle points, while true north is the location of the geographic North Pole.
Can a compas s work near metal or electronics?
No, metal objects and electronic devices can interfere with the compas s needle, causing it to give incorrect readings.
How accurate is a magnetic compas s?
A magnetic compas s is generally very accurate, but it can be affected by magnetic declination, which varies depending on your location.
What should I do if my compas s isn’t working?
Check for interference from nearby metal or electronic objects. If the compas s is still not working, it may be demagnetized or broken.
Can I use a compas s without a map?
Yes, a compas s can still help you determine direction without a map, but using it with a map provides much more precise navigation.

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year ago
 Business2 years ago
Business2 years ago
 Social Media2 years ago
Social Media2 years ago
 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years ago
 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year ago
 FOOD1 year ago
FOOD1 year ago
 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years ago
 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years ago