General
What is CMDB?
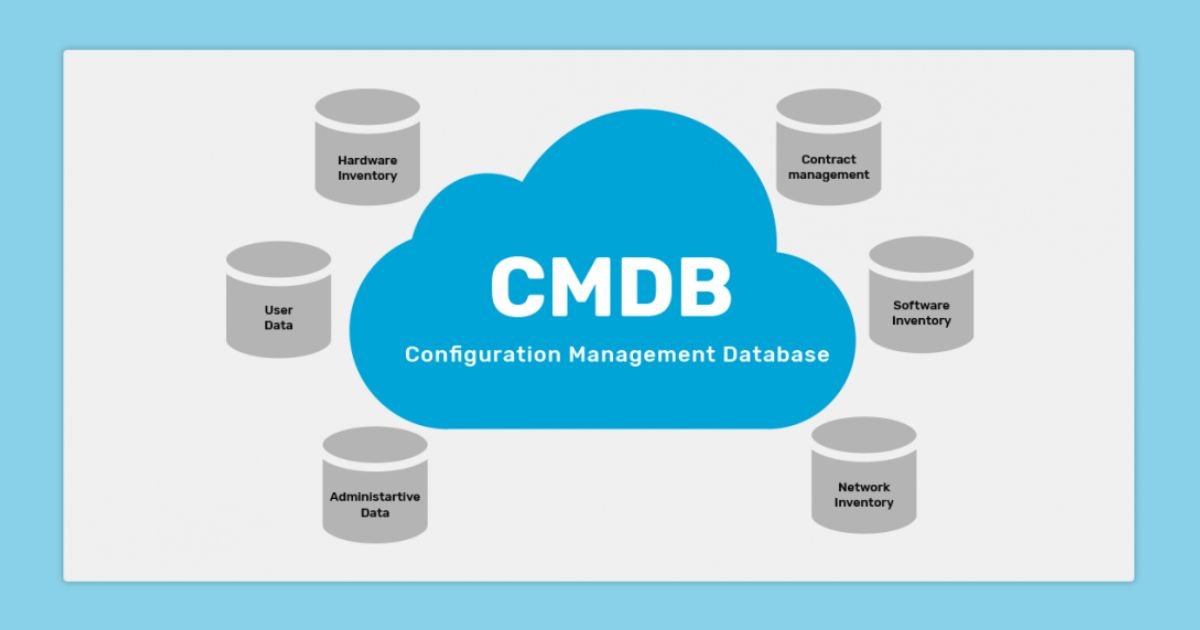
In today’s fast-paced IT environments, keeping track of all the different components that make up an organization’s infrastructure can feel like herding cats. That’s where the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) comes in. So, what is CMDB? It’s essentially a database that stores information about an organization’s IT environment. This includes hardware, software, networks, and even the relationships between these components. But CMDB isn’t just another database; it’s the backbone of IT service management (ITSM), helping businesses gain visibility, manage assets, and deliver efficient services.
A CMDB provides a single source of truth, enabling IT teams to track the complex and ever-changing nature of their systems. It helps them understand dependencies, troubleshoot issues, and even plan for future infrastructure changes. If you’re wondering how your organization can benefit from this, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into how CMDB plays a pivotal role in modern IT operations.
The Role of CMDB in IT Service Management
If your organization has embraced IT Service Management (ITSM), then CMDB is an integral piece of the puzzle. In ITSM, services like incident, problem, and change management depend heavily on understanding the relationships between different components in your IT environment. This is where CMDB shines—it links everything together.
Imagine your company’s IT system as a huge jigsaw puzzle. Without CMDB, pieces of this puzzle might be scattered around, making it difficult to see the whole picture. With CMDB, every piece is organized and documented. It shows how a failure in one system could impact another and allows you to respond proactively before issues escalate.
Key Components of CMDB
To understand CMDB better, let’s break it down into its essential components.
Configuration Items (CIs)
A Configuration Item (CI) is a core concept in CMDB. It represents an asset or entity that is part of your IT infrastructure—anything from a server, a virtual machine, or a network router, to even software and databases. Every CI contains data like specifications, ownership, and its relationship to other CIs.
Relationships between CIs
Not only does CMDB track individual CIs, but it also maps the relationships between them. For instance, if a server supports a specific application, that relationship is recorded. This level of detail is crucial during incident management, helping teams to understand root causes and their potential impact on other systems.
Data Stored in a CMDB
A CMDB holds a variety of data, including asset details (like purchase date, vendor, warranty information), performance metrics, configurations, and relationships between assets. This makes it far more than a static inventory—it’s a dynamic, living database that evolves with your infrastructure.
CMDB vs IT Asset Management
You might wonder, how is a CMDB different from IT asset management (ITAM)? While both are focused on tracking IT resources, they serve distinct purposes.
Differences between CMDB and IT Asset Management
While IT asset management focuses on the financial and contractual side of IT assets (like procurement, depreciation, and lifecycle management), CMDB is more technical. It dives deep into the configurations and relationships between assets.
In other words, IT asset management helps you track what you own, while a CMDB helps you understand how those assets work together. This is where a good it asset management solution plays a key role, complementing the CMDB to give a comprehensive overview of both financial and operational data.
How They Complement Each Other
When used together, CMDB and ITAM offer unparalleled visibility. For example, while ITAM might tell you that a server is nearing the end of its lifecycle, CMDB can show how replacing that server will affect the rest of your infrastructure. Together, they ensure smarter decision-making, especially when planning upgrades, mitigating risks, or managing budgets.
How CMDB Benefits Organizations
The benefits of having a CMDB are vast, ranging from improved infrastructure visibility to enhanced decision-making. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
Improved Visibility and Control over IT Infrastructure
One of the biggest challenges in IT is the complexity and scale of systems. A well-maintained CMDB provides a clear overview of your infrastructure, making it easier to monitor and control. This improved visibility can streamline IT operations and reduce downtime.
Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
With a comprehensive view of your IT environment, CMDB supports informed decision-making. Whether you’re planning a new project or upgrading a critical system, you can better understand potential impacts and mitigate risks beforehand.
Reducing Downtime and Accelerating Incident Management
When issues arise, CMDB helps your team act swiftly. By knowing the relationships between systems, your team can identify the root cause faster, reducing downtime and minimizing disruptions. It’s like having a roadmap when navigating a maze.
Implementing CMDB in Your Organization
So, how do you implement a CMDB? It’s not as simple as installing a piece of software. A successful CMDB requires proper planning and execution.
Steps to Successfully Implement CMDB
First, identify the configuration items that are crucial to your organization. Then, define their relationships and how they’ll be tracked. Finally, ensure the CMDB is continuously updated as your infrastructure evolves. Consistency is key.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
One common challenge is data inaccuracy. Over time, data can become outdated or incomplete. To combat this, automate updates whenever possible and schedule regular audits to keep your CMDB accurate.
Best Practices for Maintaining an Efficient CMDB
Best practices include establishing clear roles and responsibilities for maintaining the CMDB, automating where possible, and integrating the CMDB with other ITSM tools.
FAQs
1. What is a CMDB used for?
A CMDB is used to track and manage an organization’s IT infrastructure, helping to map out the relationships between various components and ensuring smooth service management.
2. How does CMDB improve IT service delivery?
CMDB improves IT service delivery by offering better visibility into infrastructure, enabling faster root-cause analysis, and enhancing change management processes.
3. Can a CMDB work without IT asset management?
Yes, a CMDB can function independently, but it works best when integrated with IT asset management for a more holistic view of both technical and financial data.
4. What are common challenges in maintaining a CMDB?
Challenges include data inaccuracy, outdated information, and lack of automation. Regular audits and integration with other tools can help keep the CMDB current.
5. How often should you update your CMDB?
Your CMDB should be updated continuously or as often as changes occur in your IT environment to ensure accuracy.
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHow to Use a Temporary Number for WhatsApp
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSepatuindonesia.com | Best Online Store in Indonesia
-

 Social Media1 year ago
Social Media1 year agoThe Best Methods to Download TikTok Videos Using SnapTik
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoTop High Paying Affiliate Programs
-

 Tech10 months ago
Tech10 months agoUnderstanding thejavasea.me Leaks Aio-TLP: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 FOOD12 months ago
FOOD12 months agoHow to Identify Pure Desi Ghee? Ultimate Guidelines for Purchasing Authentic Ghee Online
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Auto Follower Without Login
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Follower Without Login




















