Tech
Understanding The Role Of RAM In Modern Computing
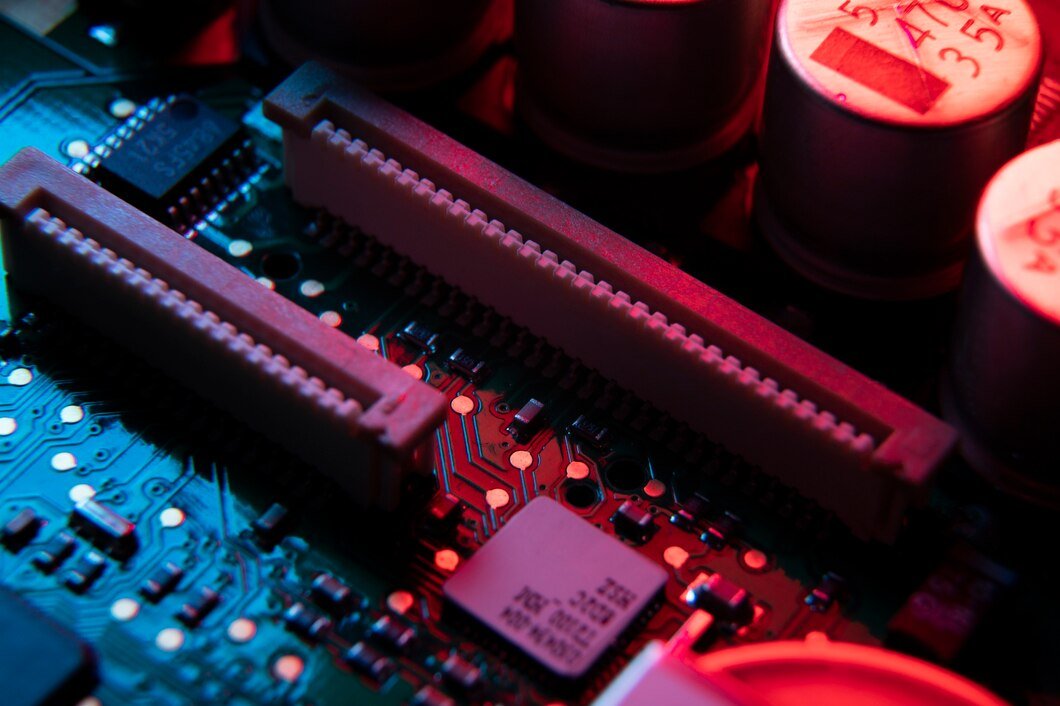
In the world of computing, Random Access Memory (RAM) is a fundamental component that significantly influences the performance of a computer system. Whether you’re using a laptop for everyday tasks or a high-end gaming rig, RAM plays a crucial role in determining how efficiently your device operates. Understanding RAM computing and its various types is essential for anyone looking to optimize their computing experience or make informed decisions about hardware upgrades. For a deeper dive into the significance of memory in PC performance, check out.
A. Brief Overview Of RAM And Its Importance In Computing
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of volatile memory that provides fast read and write access to a computer’s processor. Unlike storage devices such as hard drives or SSDs, which retain data even when the computer is turned off, RAM temporarily holds data that the CPU needs while executing tasks. This includes data from applications, operating systems, and files that are currently in use. The speed and efficiency of RAM directly affect a system’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and execute programs quickly.
II. RAM
A. Definition And Basic Concept Of RAM
RAM is a type of memory that provides a space for the CPU to read and write data needed for current tasks. It is called random access because it allows data to be read or written in any order, as opposed to sequential access memory like tape drives. The data stored in RAM is temporary and is lost when the computer is powered off, making it an essential component for active processes but not for long-term storage.
RAM’s primary function is to provide the CPU with quick access to data, enhancing the speed at which applications and processes run. This is why having more RAM typically results in better system performance, as it allows the computer to keep more data readily accessible, reducing the need to swap data in and out of slower storage.
B. Difference Between RAM And Other Types Of Memory
While RAM is crucial for active data processing, it is not the only type of memory used in computers. Other types of memory include Read-Only Memory (ROM) and cache memory, each serving different purposes.
ROM (Read-Only Memory): Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile, meaning it retains data even when the power is off. ROM is typically used to store firmware or system software that is rarely changed, such as the BIOS in a computer. It provides essential instructions for booting up the system and initializing hardware components.
Cache Memory: Cache is a smaller, faster type of volatile memory that sits between RAM and the CPU. It stores frequently accessed data and instructions to speed up processing times. Because cache memory is faster than RAM, it helps reduce the time the CPU spends waiting for data, thereby improving overall system performance.
C. Types Of RAM
RAM comes in various types, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM): This is the most prevalent form of RAM found in computers. It stores each piece of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. DRAM is affordable and provides a good balance between cost and performance, but it requires periodic refreshing to maintain data integrity.
SRAM (Static RAM): It stores data in flip-flops, which makes it faster and more reliable than DRAM. However, SRAM is more expensive and less dense, which limits its use to cache memory and other high-performance applications.
Understanding the different types of RAM and their roles helps in making informed decisions about hardware upgrades and optimizing computing performance. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of RAM and its applications will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of computing.
III. RAM And System Specifications
A. How RAM Affects Overall System Specifications
RAM computing is a critical factor in determining the overall performance of a computer system. It influences various system specifications, including benchmark scores, multitasking capabilities, and gaming performance.
System Benchmarks: Benchmarks measure a system’s performance across different tasks and applications. More RAM can lead to higher benchmark scores because it allows the CPU to access more data quickly, reducing the need for slower storage access. Systems with ample RAM tend to perform better in benchmarks that test multi-threaded processing and data-heavy applications, such as video editing and 3D rendering.
Gaming Performance: In gaming, RAM plays a significant role in determining frame rates and load times. Modern games often require substantial amounts of RAM to handle complex textures, large environments, and real-time data processing. Insufficient RAM can lead to stuttering, lag, and longer load times, detracting from the overall gaming experience. High-performance RAM enables smoother gameplay and faster data handling, which can be crucial for competitive gaming where every millisecond counts.
B. Recommended Ram Sizes For Different User Needs
The amount of RAM needed varies depending on the user’s requirements and the intended use of the computer.
Casual Users: For everyday tasks such as web browsing, word processing, and streaming media, 8GB of RAM is generally sufficient. This amount allows for smooth multitasking without significant slowdowns or interruptions.
Gamers: Gamers typically benefit from 16GB of RAM, which provides enough capacity to handle modern games and background applications simultaneously. This amount of RAM ensures that games run smoothly and reduces the risk of performance issues during intense gaming sessions.
Professionals: For users involved in professional tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, or software development, 32GB or more is recommended. These tasks require substantial memory resources for handling large files and complex operations efficiently. High RAM capacity helps in managing large datasets and running multiple resource-intensive applications without compromising performance.
IV. Advancements In RAM Technology
A. Overview Of Recent Advancements In RAM Technology
Recent advancements in RAM technology have introduced significant improvements in speed, efficiency, and functionality. Two notable advancements are DDR5 and LPDDR5.
DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5): DDR5 is the latest generation of RAM, offering substantial improvements over its predecessor, DDR4. DDR5’s enhanced performance capabilities support the demands of advanced computing tasks and future-proof systems against upcoming software requirements.
LPDDR5 (Low Power Double Data Rate 5): LPDDR5 is designed for mobile devices, offering similar improvements to DDR5 but with a focus on power efficiency. It enables faster data transfer rates while consuming less power, which is crucial for extending battery life in smartphones and laptops.
B. Benefits Of New Ram Technologies
The advancements in DDR5 and LPDDR5 technologies bring several benefits.
Faster Speeds: DDR5 and LPDDR5 offer faster data transfer rates compared to previous generations, leading to quicker access times and improved overall system performance. This speed boost is especially beneficial for high-demand applications such as gaming, virtual reality, and professional software.
Lower Power Consumption: Both DDR5 and LPDDR5 are designed to be more energy-efficient. DDR5’s improved power management features help reduce energy consumption, while LPDDR5’s low power usage extends battery life in mobile devices. These efficiency gains contribute to longer device lifespan and lower operating costs.
V. Conclusion
RAM is a fundamental element of modern computing that continues to evolve alongside technological advancements. Its ongoing importance and the exciting potential for future developments highlight the need for users and professionals alike to stay informed about RAM technology. For instance, understanding whether you can run your RAM at its maximum speed is crucial for optimizing performance. As we move forward, RAM will remain a key player in enabling the next generation of high-performance RAM computing and emerging technological breakthroughs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How does RAM differ from other types of memory?
RAM is faster and used for temporary storage of active data, while ROM (Read-Only Memory) and cache memory serve different purposes. ROM is non-volatile and stores firmware, while cache memory is a smaller, faster type of volatile memory used to speed up data access for the CPU.
2. Why is RAM important for my computer’s performance?
RAM is crucial for performance as it allows the CPU to quickly access and process data. More RAM enables better multitasking, faster application performance, and smoother operation of demanding software.
3. How much RAM do I need for typical tasks?
For basic tasks such as web browsing and word processing, 8GB of RAM is generally sufficient. For gaming or professional applications like video editing, 16GB to 32GB may be recommended to ensure optimal performance.
4. What are the latest advancements in RAM technology?
Recent advancements include DDR5 and LPDDR5 RAM, which offer higher speeds, greater bandwidth, and improved energy efficiency compared to previous generations.
5. Can having more RAM always improve my computer’s speed?
Not always. While having more RAM can improve performance, it only benefits applications and processes that need it. If your system already has enough RAM for your tasks, adding more may not result in noticeable performance gains.
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHow to Use a Temporary Number for WhatsApp
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSepatuindonesia.com | Best Online Store in Indonesia
-

 Social Media2 years ago
Social Media2 years agoThe Best Methods to Download TikTok Videos Using SnapTik
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoTop High Paying Affiliate Programs
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoUnderstanding thejavasea.me Leaks Aio-TLP: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 FOOD1 year ago
FOOD1 year agoHow to Identify Pure Desi Ghee? Ultimate Guidelines for Purchasing Authentic Ghee Online
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Auto Follower Without Login
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Follower Without Login