Travel
The Fascinating World of Antiquità: Discovering Ancient Treasures
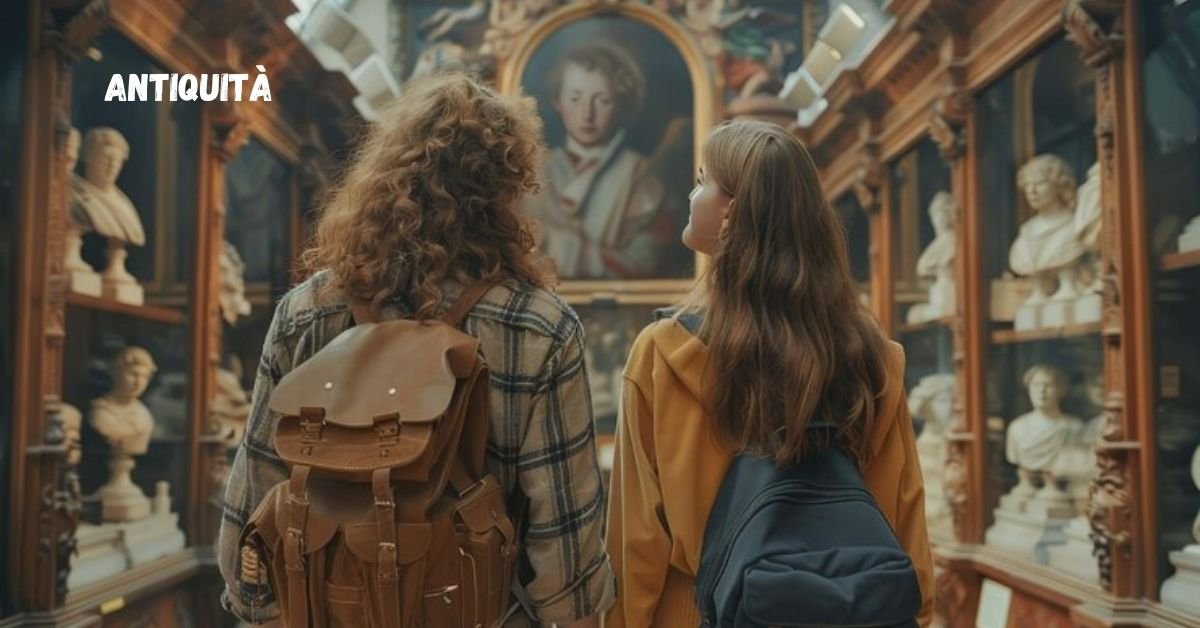

Antiquità, the Italian word for antiquities, refers to ancient artifacts, relics, and cultural treasures that provide a glimpse into the past. These items, ranging from everyday objects to monumental structures, offer valuable insights into the civilizations that created them. Exploring the world of antiquità allows us to connect with history, understand cultural evolution, and appreciate the artistry and craftsmanship of bygone eras.
The Significance of Antiquità
Antiquities hold immense historical value. They are tangible links to the past, providing evidence of human activity, societal structures, and technological advancements. Each artifact tells a story, offering clues about the people who made and used it. By studying these objects, historians and archaeologists can piece together narratives of ancient civilizations, shedding light on their customs, beliefs, and daily lives.
Types of Antiquità
Antiquità encompasses a wide variety of items. These include pottery, sculptures, jewelry, coins, tools, and manuscripts. Architectural structures such as temples, tombs, and amphitheaters are also considered antiquities. Each type of artifact offers unique insights into different aspects of ancient life, from domestic routines to religious practices.
Pottery and Ceramics
Pottery is one of the most common types of antiquities. Ancient pottery includes everyday items like bowls, jars, and vases, as well as ceremonial pieces. The study of pottery helps archaeologists understand trade, dietary habits, and technological advancements in ancient societies. The styles and techniques used in pottery making also provide information about cultural influences and artistic trends.
Sculptures and Statues
Sculptures and statues are iconic representations of antiquità. These artworks range from small figurines to colossal statues. They often depict deities, rulers, and mythological figures, reflecting the religious and cultural beliefs of the time. The materials used, such as marble, bronze, and terracotta, reveal information about the resources available and the technological capabilities of ancient artisans.
Jewelry and Adornments
Ancient jewelry and adornments offer insights into fashion, social status, and cultural practices. These items, made from materials like gold, silver, and gemstones, showcase the craftsmanship and artistic skills of ancient jewelers. The designs and motifs used in jewelry can also indicate trade relationships and cultural exchanges between different regions.
Coins and Currency
Coins are valuable sources of historical information. They often feature portraits of rulers, inscriptions, and symbols, providing insights into political and economic systems. The study of ancient coins, known as numismatics, helps historians understand trade networks, monetary policies, and historical events.
Tools and Implements
Ancient tools and implements reveal technological advancements and everyday activities. These items include farming equipment, weapons, and household tools. Studying these artifacts helps us understand how ancient people lived, worked, and interacted with their environment.
Manuscripts and Inscriptions
Manuscripts and inscriptions are vital for understanding ancient languages, literature, and administrative practices. These texts, written on materials like papyrus, parchment, and stone, provide direct evidence of communication, record-keeping, and cultural expressions. They offer valuable insights into the intellectual and cultural achievements of ancient civilizations.
Architectural Antiquities
Architectural structures are among the most impressive antiquities. Temples, tombs, amphitheaters, and other monumental buildings reveal the architectural prowess and religious beliefs of ancient societies. These structures often served as centers of worship, entertainment, and governance, reflecting the social and political dynamics of the time.
Preservation and Conservation
The preservation and conservation of antiquità are crucial for safeguarding cultural heritage. Many ancient artifacts are vulnerable to environmental factors, looting, and neglect. Efforts to protect and restore these treasures ensure that future generations can continue to learn from and appreciate them. Conservation techniques include stabilization, cleaning, and environmental control to prevent further deterioration.
Ethical Considerations
The collection and trade of antiquities raise ethical concerns. The looting of archaeological sites and the illicit trade of artifacts deprive countries of their cultural heritage and disrupt historical research. International laws and conventions aim to protect antiquities and promote the ethical acquisition and repatriation of cultural property. Responsible collecting and adherence to legal frameworks are essential for preserving the integrity of historical artifacts.
The Role of Museums
Museums play a vital role in the preservation and interpretation of antiquità. They provide safe environments for the display and study of ancient artifacts. Museums also offer educational programs and exhibitions that engage the public with history and archaeology. By making antiquities accessible to a wide audience, museums contribute to cultural awareness and appreciation.
The Future of Antiquità Studies
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing the study of antiquità. Techniques such as 3D scanning, digital imaging, and remote sensing allow for detailed analysis and documentation of artifacts. These tools enable researchers to uncover new information and share their findings with a global audience. The use of technology also enhances conservation efforts, ensuring the long-term preservation of ancient treasures.
Engaging with Antiquità
Engaging with antiquità is a rewarding experience that connects us to our shared human heritage. Visiting archaeological sites, exploring museum collections, and participating in educational programs provide opportunities to learn about ancient civilizations. By appreciating and preserving antiquities, we honor the achievements of our ancestors and enrich our understanding of history.
Conclusion
The world of antiquità offers a captivating journey into the past, revealing the rich tapestry of human history through ancient artifacts and relics. These treasures provide invaluable insights into the lives, beliefs, and achievements of our ancestors. By studying and preserving antiquities, we honor the legacy of past civilizations and deepen our understanding of our shared heritage. As we continue to explore, conserve, and ethically engage with these ancient treasures, we ensure that the stories of antiquità will inspire and educate future generations.
FAQs
What is the importance of studying antiquità?
Studying antiquities helps us understand the history, culture, and technological advancements of ancient civilizations. It provides insights into the daily lives, beliefs, and artistic achievements of our ancestors.
How are antiquities preserved and conserved?
Antiquities are preserved through stabilization, cleaning, and environmental control. Conservation efforts aim to prevent further deterioration and protect artifacts from damage caused by environmental factors and human activities.
What ethical considerations are involved in the collection of antiquities?
Ethical considerations include preventing looting and the illicit trade of artifacts. International laws and conventions promote the ethical acquisition and repatriation of cultural property to protect the integrity of historical artifacts.
How do museums contribute to the preservation of antiquities?
Museums provide safe environments for the display and study of ancient artifacts. They offer educational programs and exhibitions that engage the public with history and archaeology, contributing to cultural awareness and appreciation.
What role does technology play in the study of antiquities?
Advancements in technology, such as 3D scanning and digital imaging, allow for detailed analysis and documentation of artifacts. These tools enhance research, conservation efforts, and the sharing of findings with a global audience.
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHow to Use a Temporary Number for WhatsApp
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSepatuindonesia.com | Best Online Store in Indonesia
-

 Social Media2 years ago
Social Media2 years agoThe Best Methods to Download TikTok Videos Using SnapTik
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoTop High Paying Affiliate Programs
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoUnderstanding thejavasea.me Leaks Aio-TLP: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 FOOD1 year ago
FOOD1 year agoHow to Identify Pure Desi Ghee? Ultimate Guidelines for Purchasing Authentic Ghee Online
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Auto Follower Without Login
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Follower Without Login