Technology
How to Recycle Household Batteries: Your Complete Guide to Responsible Disposal
Why Battery Recycling Isn’t Optional Anymore
Every year, Americans throw away 3 billion batteries, with most ending up in landfills where they leak toxic materials into soil and groundwater. But here’s what most people don’t know – battery recycling is easier than ever, often free, and some programs even pay you for certain battery types.
After researching recycling programs nationwide and interviewing facility operators, we’ve created this comprehensive guide to help you recycle batteries responsibly. Whether you have a drawer full of dead batteries or just want to establish good habits, this guide shows you exactly what to do.
Understanding Which Batteries Can Be Recycled
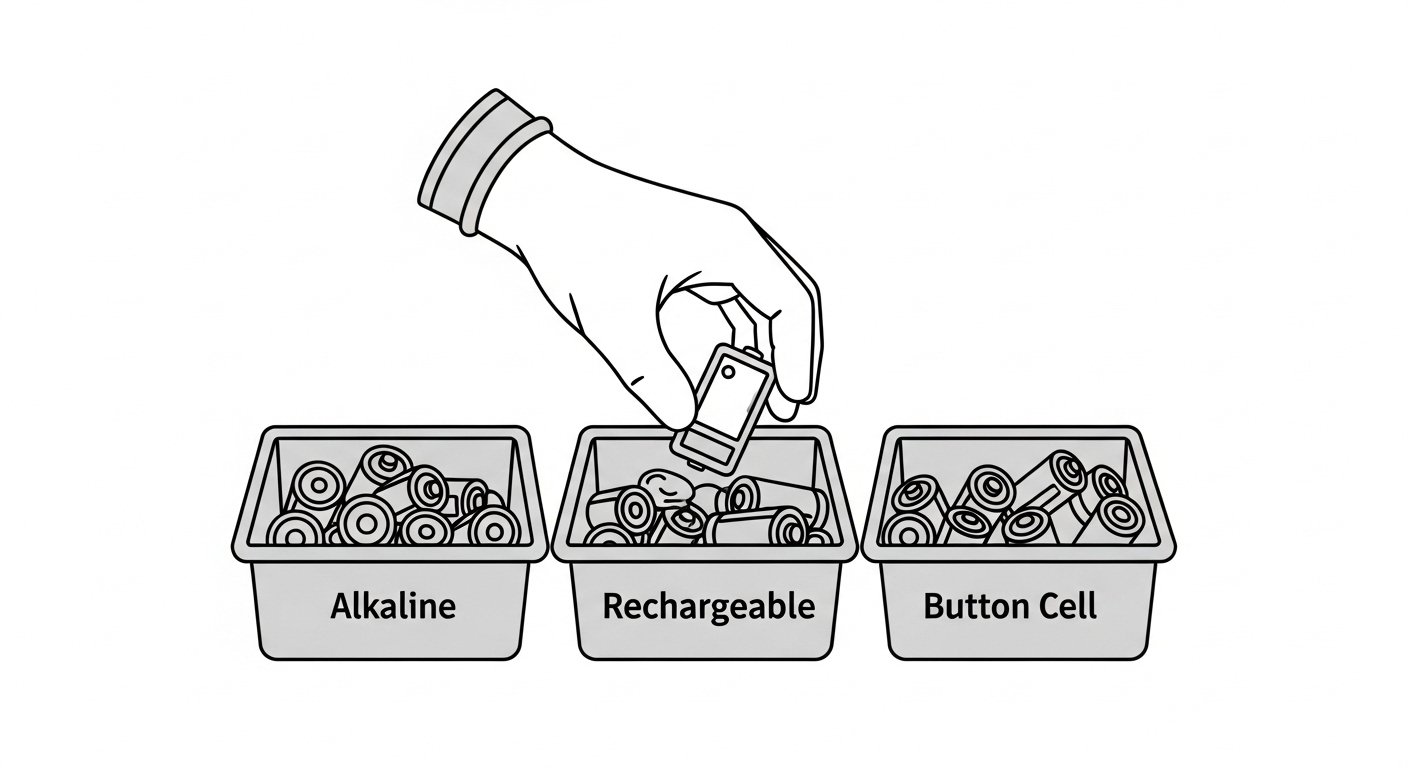
Not all batteries recycle the same way, and mixing types can create safety hazards at recycling facilities.
Easily recyclable batteries:
- All rechargeable batteries (lithium-ion, NiMH, NiCd)
- Lead-acid batteries (car batteries)
- Lithium primary batteries
- Button cell batteries
- Specialty batteries (medical, military)
Recycling challenges:
- Alkaline batteries (accepted some places, not others)
- Zinc-carbon batteries (limited recycling value)
- Damaged or swollen batteries (require special handling)
The good news? 99% of battery materials can be recovered and reused. One ton of recycled batteries yields enough materials to make 1,800 new batteries.
Finding Battery Recycling Locations Near You
Multiple options exist for battery recycling, often within minutes of your home:
Retail drop-off programs:
- Home Depot: All stores accept rechargeable batteries
- Lowe’s: Rechargeable battery recycling bins at entrances
- Best Buy: Accepts all battery types, limit 3 per day
- Staples: Free recycling for rechargeable batteries
- Target: Select stores have battery recycling kiosks
Call2Recycle locations:
The largest battery recycling program in North America with 30,000 drop-off locations. Visit call2recycle.org and enter your ZIP code to find nearby locations. Most accept all household batteries free of charge.
Municipal programs:
- Household hazardous waste (HHW) facilities
- Special collection events (usually quarterly)
- Curbside pickup (in select cities)
- Transfer stations and recycling centers
- Library and community center drop-boxes
Voniko partners with recycling programs nationwide, providing prepaid shipping labels for bulk battery recycling.
Preparing Batteries for Recycling
Proper preparation prevents fires and ensures safe handling:
Essential preparation steps:
- Sort batteries by type (alkaline, lithium, rechargeable)
- Tape terminals with clear packing tape
- Place in separate plastic bags by type
- Label bags clearly
- Never mix damaged batteries with intact ones
- Keep batteries dry
For damaged or swollen batteries:
- Place individually in plastic bags
- Add sand or kitty litter to the bag
- Label as “damaged battery”
- Transport separately from other batteries
- Inform recycling center staff
Terminal taping technique:
Cover both ends of cylindrical batteries and all terminals on flat batteries. This prevents short circuits during transport and processing.
The Recycling Process: What Actually Happens
Understanding the recycling process shows why proper sorting matters:
Step 1: Collection and sorting
Batteries arrive at processing facilities where workers sort them by chemistry. Improper sorting can cause fires or contaminate recycling streams.
Step 2: Mechanical processing
Batteries are crushed in specialized equipment that captures gases and prevents reactions. Different battery types require different processes.
Step 3: Material separation
- Plastics separated for recycling
- Metals extracted through various processes
- Electrolytes neutralized or recovered
- Rare materials isolated for reuse
Step 4: Material refinement
Recovered materials are refined to battery-grade quality. Lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other materials return to battery manufacturing.
Recovery rates:
- Lead-acid: 99% material recovery
- Lithium-ion: 95% material recovery
- NiMH: 90% material recovery
- Alkaline: 100% material recovery (where accepted)
Special Recycling Programs and Incentives
Several programs offer incentives or special services:
Manufacturer take-back programs:
- Tesla: Accepts all lithium-ion batteries, not just their own
- Apple: Trade-in credit for device batteries
- Samsung: Mail-back program for all batteries
- Duracell: Sponsors local collection events
Paid recycling programs:
- Car batteries: $5-15 at auto parts stores
- Large lithium packs: Scrap value paid by weight
- Bulk quantities: Some recyclers pay for sorted batteries
- Corporate programs: Tax deductions for businesses
Specialty programs:
- Medical device batteries: Hospitals often accept returns
- Power tool batteries: Hardware stores take brand trade-ins
- E-bike batteries: Bike shops handle recycling
- Hearing aid batteries: Audiologists collect for recycling
State-by-State Recycling Requirements
Battery recycling laws vary significantly:
Mandatory recycling states:
- California: Illegal to dispose of any batteries in trash
- New York: Retailers must accept rechargeable batteries
- Vermont: Producer responsibility for all batteries
- Minnesota: Retailers selling batteries must offer recycling
Voluntary programs:
Most states rely on voluntary programs but may have specific requirements for businesses or certain battery types.
Future legislation:
By 2026, expect federal battery recycling standards as part of infrastructure and climate initiatives.
Creating a Home Battery Recycling System
Establish an efficient home recycling system:
Setting up your system:
- Designate a battery recycling container
- Use divided organizers for sorting
- Keep tape readily available
- Post recycling location information
- Schedule quarterly recycling trips
Container recommendations:
- Plastic storage box with lid
- Divided sections for battery types
- Clear labeling system
- Store in cool, dry location
- Child-proof if necessary
Making it convenient:
Place collection containers where batteries are commonly used – kitchen, garage, home office. The easier the system, the more likely family members will use it.
Business and Bulk Battery Recycling
Businesses have additional recycling options and sometimes obligations:
Commercial recycling services:
- Battery Solutions: Nationwide mail-back programs
- Call2Recycle: Business membership programs
- Veolia: On-site pickup for large quantities
- Heritage Environmental: Certified recycling services
Bulk recycling costs:
- Small quantities (under 50 lbs): Often free
- Medium quantities (50-500 lbs): $0.50-1.50 per pound
- Large quantities (over 500 lbs): $0.25-0.75 per pound
- Sorted batteries: 20-30% lower costs
Documentation provided:
- Certificates of recycling
- Chain of custody documentation
- Environmental compliance reports
- Tax deduction receipts
Companies like Highstar offer take-back programs for their industrial customers.
Environmental Impact of Battery Recycling
The numbers tell a compelling story:
Materials recovered annually in US:
- 180,000 tons of battery materials recycled
- Enough lithium for 200,000 EV batteries
- Cobalt to make 1 million smartphones
- Lead for 5 million car batteries
Environmental benefits:
- 70% less energy than mining new materials
- 90% reduction in greenhouse gases
- Prevents 500,000 tons of toxins from landfills
- Conserves finite natural resources
What happens without recycling:
- Heavy metals contaminate groundwater
- Lithium fires in landfills
- Toxic air emissions from incineration
- Loss of valuable materials
Every battery you recycle makes a measurable difference.
Common Recycling Mistakes to Avoid
Learn from others’ errors:
Never do this:
- Don’t throw batteries in regular recycling bins
- Don’t mix battery types in one container
- Don’t recycle batteries with regular electronics
- Don’t remove labels from specialty batteries
- Don’t attempt to disassemble batteries
- Don’t store large quantities at home
Safety mistakes:
- Failing to tape terminals
- Recycling damaged batteries with good ones
- Using metal containers for collection
- Leaving batteries in hot cars before recycling
- Accumulating batteries for years
International Battery Recycling Comparison
The US lags behind other countries:
Leading countries:
- Switzerland: 75% battery recycling rate
- Germany: 70% recycling rate
- Belgium: 65% recycling rate
- USA: 25% recycling rate
Why others succeed:
- Mandatory producer responsibility
- Convenient collection infrastructure
- Financial incentives for consumers
- Public education campaigns
- Standardized national programs
The EU requires 65% battery recycling by 2025. The US has no federal requirement.
The Economics of Battery Recycling
Understanding the economics explains program limitations:
Value by battery type:
- Lead-acid: $0.20-0.40 per pound
- Lithium-ion: $0.50-2.00 per pound
- NiMH: $3.00-5.00 per pound
- Alkaline: -$0.05 per pound (costs money to recycle)
Why some programs limit alkaline:
Alkaline batteries cost more to recycle than their materials are worth. Programs accepting them subsidize recycling through other battery types or grants.
Future economics:
As raw material prices rise and recycling technology improves, expect all battery recycling to become profitable by 2030.
Special Considerations for Different Battery Types
Each battery type has specific recycling requirements:
Car batteries:
- Return to auto parts stores for core credit
- Never put in regular recycling
- Transport upright to prevent acid leaks
- Most valuable batteries to recycle
Laptop/phone batteries:
- Often accepted at electronics stores
- May have trade-in value
- Remove from devices if possible
- Check manufacturer programs first
Power tool batteries:
- Hardware stores often accept same-brand returns
- Some offer credit toward new batteries
- Valuable materials make recycling profitable
- Consider rebuilding services
Button batteries:
- Extremely important to recycle (mercury content)
- Pharmacies often collect them
- Hearing aid centers accept all brands
- Tape both sides before recycling
Making Battery Recycling a Habit
Transform good intentions into consistent action:
Building the habit:
- Start with one collection container
- Set phone reminders for recycling trips
- Combine with other errands
- Involve entire family
- Track quantities recycled
- Celebrate milestones
Teaching children:
- Explain why recycling matters
- Make them recycling helpers
- Show the recycling process
- Reward participation
- Lead by example
Community involvement:
- Organize building collection programs
- Share recycling information on social media
- Volunteer at collection events
- Advocate for better programs
- Start workplace initiatives
Future of Battery Recycling
Exciting developments are coming:
Technology improvements:
- AI-powered sorting systems
- Direct recycling preserving cathode structures
- Biological recycling using bacteria
- Automated disassembly systems
- Blockchain tracking of materials
Program expansion:
- Curbside battery pickup expanding
- Retailer programs becoming universal
- Mail-back programs simplifying the process
- Financial incentives increasing
- Federal standards developing
Circular economy:
By 2030, expect closed-loop systems where every battery sold contains recycled materials from previous batteries.
Your Battery Recycling Action Plan
Start recycling batteries today:
- Gather all dead batteries from drawers, devices, and storage areas
- Sort by type using our guide
- Tape terminals with clear packing tape
- Find nearest drop-off using Call2Recycle.org
- Set up home collection system
- Schedule regular recycling trips
- Share this guide with others
Small actions multiply. If every household recycled just 10 batteries yearly, we’d keep 300 million batteries from landfills.
FAQs
Is it really worth the effort to recycle batteries?
Absolutely. One recycled laptop battery provides enough cobalt for 50 new smartphone batteries. Recycling prevents toxic materials from contaminating water supplies and recovers valuable materials that would otherwise require environmentally destructive mining.
Can I make money recycling batteries?
Car batteries typically fetch $5-15 at auto parts stores. Some scrap yards pay for large quantities of lithium-ion batteries. While household battery recycling rarely pays directly, you’re saving environmental cleanup costs that eventually affect everyone through taxes and health costs.
What happens if batteries aren’t recycled properly?
Batteries in landfills leak heavy metals into groundwater, contaminating drinking water sources. Lithium batteries cause fires in garbage trucks and landfills. Incinerated batteries release toxic gases. The environmental damage costs billions in cleanup and health impacts.
Why do some places not accept alkaline batteries for recycling?
Alkaline batteries cost more to recycle than their materials are worth (about $0.05 loss per battery). Some programs can’t afford this subsidy. However, alkaline batteries are less toxic than other types and some states allow landfill disposal.
How long can I store dead batteries before recycling?
Store dead batteries up to one year safely if kept cool, dry, and with terminals taped. However, recycle every 3-6 months to prevent accumulation. Damaged or swollen batteries should be recycled immediately as they pose fire risks.
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHow to Use a Temporary Number for WhatsApp
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSepatuindonesia.com | Best Online Store in Indonesia
-

 Social Media2 years ago
Social Media2 years agoThe Best Methods to Download TikTok Videos Using SnapTik
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoTop High Paying Affiliate Programs
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoUnderstanding thejavasea.me Leaks Aio-TLP: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 FOOD1 year ago
FOOD1 year agoHow to Identify Pure Desi Ghee? Ultimate Guidelines for Purchasing Authentic Ghee Online
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Auto Follower Without Login
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Follower Without Login