Health
What Core Ingredients Make Smart Cities the Future of Equitable Healthcare?
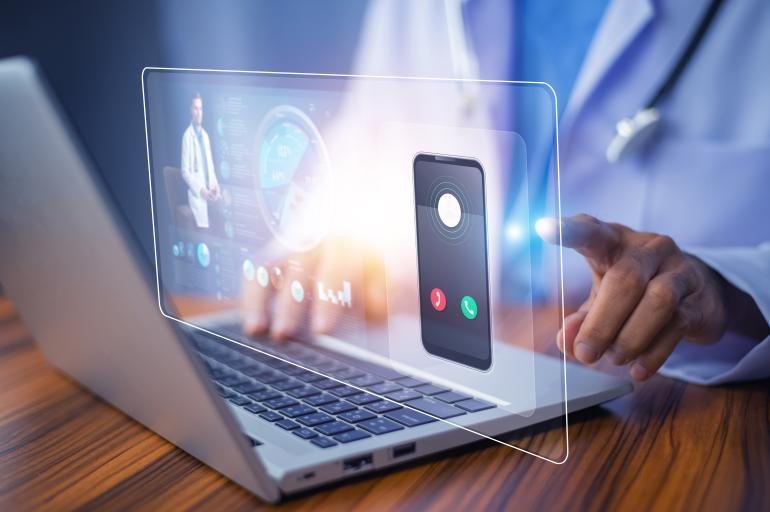

The notion of smart cities has long been linked with progress in technology and innovation. This has strived to transform city life by embracing digitalization, streamlining processes, and promoting sustainability. Such cities utilize data, artificial intelligence, and a range of digital solutions to maximize efficiency, enhance public services, and enhance the well-being of their inhabitants.
Yet, as the smart city paradigm progresses, there’s an increasing acknowledgment of the importance of extending these urban advancements beyond technological upgrades. The aim here is to tackle broader social goals, notably equity, and inclusivity. This transition signifies the shift from smart cities to equitable cities.
People-centric urban development makes sure that everyone’s lives are improved in a real way, rather than just putting effective technologies into place. This specifically applies to the field of healthcare. Even though everyone has the fundamental right to healthcare, not everyone has equal access to high-quality medical facilities, especially in cities. Recognizing this gap, smart cities work to bring together innovation and inclusivity into the healthcare industry and change it completely.
Fostering Equity in Healthcare: Key Elements in Smart City Healthcare
The concept of a “smart city” combines digitization, efficient procedures, and sustainability to improve urban living. Undeniably, providing equitable access to resources and services for all citizens is just as important as technological innovation.
This shift is particularly significant within the world of equity in healthcare. Here’s how:
1. Telemedicine & Remote Monitoring
A recent survey has projected that telemedicine has achieved an overall adoption rate of 80%. It emerged as the preferred channel for prescription care and addressing minor illnesses in 2022.
Telemedicine can surely redefine equity in healthcare by offering virtual care and monitoring patients’ health remotely. These solutions improve patient convenience while empowering healthcare technology solutions to properly monitor chronic illnesses and give therapies promptly. These technologies are essential for increasing access to healthcare, particularly in underprivileged populations, in smart cities where access to traditional healthcare services may be restricted.
Healthcare professionals can bridge geographical barriers, offer medical consultations, and provide continuous care management by leveraging telemedicine and remote monitoring. This ultimately improves health outcomes and reduces healthcare disparities.
2. AI-Driven Impactful Data Analysis
Smart cities use different data sources, like wearable technology, Internet of Things sensors, electronic health records, and socioeconomic determinants of health to obtain the large amount of data they have requirements for. Also, advanced AI-driven analytics can be employed by healthcare professionals and city owners to derive meaningful information regarding the health trends in a particular locality and to emphasize the regions where the most crucial health problems are detected with special treatment approaches.
For instance, AI-driven analysis of data from fitness trackers, public health records, and air quality monitors can unveil intricate relationships between environmental factors and health outcomes, such as the correlation between respiratory illnesses and air pollution levels. Armed with this knowledge, healthcare technology solution providers and municipal planners can implement proactive measures, such as enforcing stricter emission regulations in pollution hotspots or delivering tailored health education programs to vulnerable populations.
3. Infrastructure and Transportation
The transportation infrastructure is one of the most crucial aspects that determines access to healthcare. Strategic investments in transportation by smart cities will ensure that all of the citizens have good mobility networks to guarantee that they have equal access to medical care.
- Improved Public Transport: Smart cities put people in a position to have healthcare facilities on their doorsteps at all times by placing emphasis on equal access to public transportation.
- Pedestrian-Friendly Design: Providing walkable areas with crosswalks, safe sidewalks, and pedestrian signals can inspire pedestrians to walk to their healthcare appointments, which can promote accessibility to medical services
- Integrated Planning: Smart cities establish different location information of health facilities about the local transport infrastructure including bus routes and bike lanes, creating a clear connection among them. This model of collaboration guarantees individuals living in any corner of the city still have the same possibilities to get the support they need.
Smart cities understand how important transportation infrastructure is for people to obtain equity in healthcare. They aim to resolve transportation problems and bring about better health results for everybody to realize this through providing funding for public transportation means, setting up networks of bike lanes and roadways, persuading architects to make their cities pedestrian-friendly, and managing transportation plans.
4. Public Health Surveillance and Response
Predictive analytics and intelligent monitoring systems abound in smart cities, and they may be utilized to identify disease outbreaks. This is how these cities can identify the targeted areas where the outbreaks will mostly occur and act swiftly keeping in mind that the disease might be spreading out of control.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 75% of all emerging infectious diseases originate in animals before spilling over to humans. Smart cities utilize surveillance technologies to track potential zoonotic diseases, minimizing the risk of outbreaks and safeguarding public health.
5. Equitable Access to Digital Health Services
It is essential to achieve digital health equality to avoid the deviation in healthcare access in an environment which is getting smarter. Smart cities are not only harnessing digital infrastructure but also undertaking initiatives to overcome the digital divide. This is how the smart city solutions guarantee that every resident can benefit from telemedicine, electronic health records, and other digital health solutions.
Cities aim to create a healthcare landscape where technology serves as an equalizer by prioritizing such investments. This empowers all individuals to access essential medical services regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status.
Bottom Line
The health of their inhabitants stands as a cornerstone in the quest for thriving cities. Now, it is important to envision the evolution of Smart Cities and the emergence of health-centric solutions with the capacity to integrate new technologies into urban planning. The escalating impact of climate change on global urban populations heightens the urgency for smart interventions. Hence, it is possible to lay the foundation for resilient urban environments by conscientiously weaving data and connectivity into healthcare systems accessible to all urban demographics.
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHow to Use a Temporary Number for WhatsApp
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoSepatuindonesia.com | Best Online Store in Indonesia
-

 Social Media2 years ago
Social Media2 years agoThe Best Methods to Download TikTok Videos Using SnapTik
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoTop High Paying Affiliate Programs
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoUnderstanding thejavasea.me Leaks Aio-TLP: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 FOOD1 year ago
FOOD1 year agoHow to Identify Pure Desi Ghee? Ultimate Guidelines for Purchasing Authentic Ghee Online
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Auto Follower Without Login
-

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoFree Instagram Follower Without Login